a. Chain isomerism :- same molecular formula but different arrangements.
b. Position isomerism :- same molecular formula, same functional groups but in different positions.
c. Functional group isomerism :- same molecular formula, but different functional groups.
a. Diastereomerism (Geometrical) :- Arising of 2 different isomers because of σ bond cannot rotate about its axis (existence of the π electron cloud).
- Trans isomer is more stable than the cis isomer. As trans has low steric hindrance and 0 dipole moment.
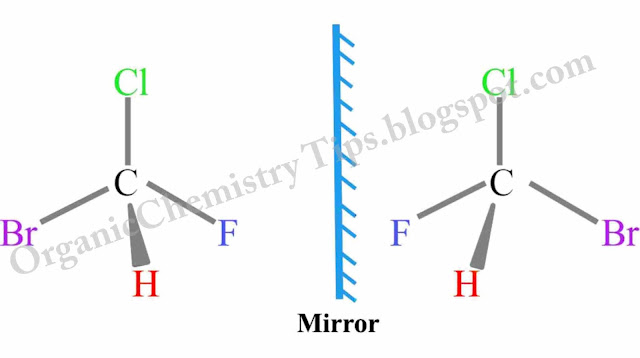
b. Enantiomerism (Optical) :- 4 different groups attached to the same carbon atom. Arising of 2 different isomers as one doesn’t superimpose with its mirror image. It and its non- Superimposable mirror image are the Enantiomers.
- Enantiomers are identified by sending plane polarized light. It and its non-superimposable mirror image rotate in 2 opposite directions.(clockwise & anti-clockwise)